This guide will walk you through building a simple yet powerful text summarizer. We will use the transformers library from Hugging Face, which provides pre-trained models capable of understanding and condensing text into a concise summary.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure you have the following:
- Python: A recent version of Python installed on your system.
- Basic Understanding of Python: You should be comfortable with basic programming concepts.
- Familiarity with Libraries: A general idea of how to install and use Python libraries.
Step 1: Set Up the Environment
First, you need to install the necessary libraries. The primary library is transformers, and it requires a deep learning framework like PyTorch (torch) or TensorFlow. The guide uses PyTorch.
Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
<pre> pip install transformers torch </pre>
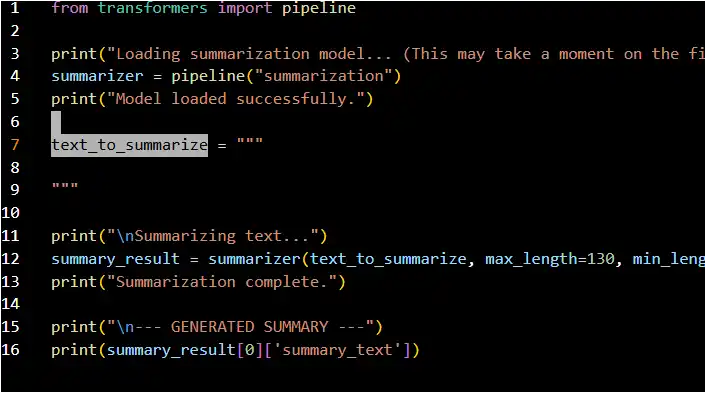
Step 2: The Complete Python Code
Here is the full Python script to perform the text summarization. It initializes a summarization “pipeline,” which handles loading the pre-trained model and tokenizer for you.
You can copy and paste this code into a Python file (e.g., summarizer.py).
<pre>
- 1. Import the pipeline function from the transformers library
from transformers import pipeline
- 2. Initialize the summarization pipeline
This will download and cache a pre-trained model for summarization.
summarizer = pipeline(“summarization”)
3. Define the long text you want to summarize
This is an example article about the importance of bees.
long_text = “”” Pollination is a vital process for the reproduction of most flowering plants and is essential for the production of a significant portion of the food we eat. Bees are arguably the most important pollinators in the world. As they travel from flower to flower to collect nectar and pollen for their hives, they inadvertently transfer pollen grains, facilitating fertilization. This process is crucial for the production of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Economically, bee pollination is invaluable. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, approximately 75% of the world’s food crops depend to some extent on pollination. This includes crops like almonds, apples, blueberries, cucumbers, and coffee. The economic value of global crops pollinated by bees and other pollinators is estimated to be hundreds of billions of dollars annually. Without bees, farmers would face significantly lower yields, leading to food shortages and increased prices.
However, bee populations are facing numerous threats. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture, pesticide use, climate change, and diseases are all contributing to a decline in bee numbers, a phenomenon known as Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD). The loss of these crucial pollinators poses a serious risk to global food security and ecosystem stability. Conservation efforts, including creating pollinator-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, and promoting sustainable agriculture, are essential to protect these vital insects. “””
4. Generate the Summary
You can adjust the max_length and min_length parameters to control the output.
summary = summarizer(long_text, max_length=130, min_length=30, do_sample=False)
5. Print the Result
The output is a list containing a dictionary. We extract the ‘summary_text’.
print(summary[0][‘summary_text’]) </pre>
Step 3: Run the Script and See the Result
To run the script, save it and execute it from your terminal:
<pre> python summarizer.py </pre>
Expected Output:
The output will be a condensed version of the long_text you provided. For the example text above, the summary would look something like this:
Bees are arguably the most important pollinators in the world . Bee pollination is invaluable to the production of a significant portion of the food we eat . The economic value of global crops pollinated by bees and other pollinators is estimated to be hundreds of billions of dollars annually . But bee populations are facing numerous threats, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change .

Code and Parameter Breakdown
The script is straightforward, but understanding its components is key.
| Code Snippet | Description |
from transformers import pipeline | Imports the essential pipeline function, which is the easiest way to use pre-trained models for various tasks. |
summarizer = pipeline("summarization") | Creates a summarization pipeline. It automatically downloads a default model (like BART) fine-tuned for this task. |
summary = summarizer(...) | This is the function call that performs the summarization on your text. |
max_length | An integer that sets the maximum number of words for the generated summary. |
min_length | An integer that sets the minimum number of words for the generated summary. |
do_sample=False | This parameter controls the generation strategy. False makes the output deterministic (it will be the same every time). |
print(summary[0]['summary_text']) | The pipeline returns a list containing a dictionary. The actual summary text is stored under the summary_text key. |
By following these steps, you have successfully built the AI-powered text summarizer described in the guide. You can now replace the long_text with any other text you wish to summarize.
from transformers import pipeline
print("Loading summarization model... (This may take a moment on the first run)")
summarizer = pipeline("summarization")
print("Model loaded successfully.")
text_to_summarize = """
"""
print("\nSummarizing text...")
summary_result = summarizer(text_to_summarize, max_length=130, min_length=30, do_sample=False)
print("Summarization complete.")
print("\n--- GENERATED SUMMARY ---")
print(summary_result[0]['summary_text'])
More Topics
- How to Showcase Your Python Skills with Mini-Projects
- How to Level Up with Advanced Python Programming Concepts
- How to Use Python for Cybersecurity Tasks
- How to Use Python for Data Science and Machine Learning
- How to Organize Your Code with Python Functions and Modules
- How to Work with Files in Python
- How to Use Python’s Core Data Structures