Of course. Here is an expanded guide on getting started with an open serverless platform, following your established formatting preferences with code blocks placed inside tables.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 How to Get Started with Apache OpenServerless
- 1.2 🧭 How to Understand the Serverless Model
- 1.3 ⚙️ How to Install and Configure
- 1.3.1 Prerequisites
- 1.3.2 Installation and Configuration Steps
- 1.4 📌 How to Explore AI Integration
- 1.4.1 Why Self-Hosted Serverless AI?
- 1.5 Writing and Deploying Your First Function
- 1.6 More Topics
How to Get Started with Apache OpenServerless
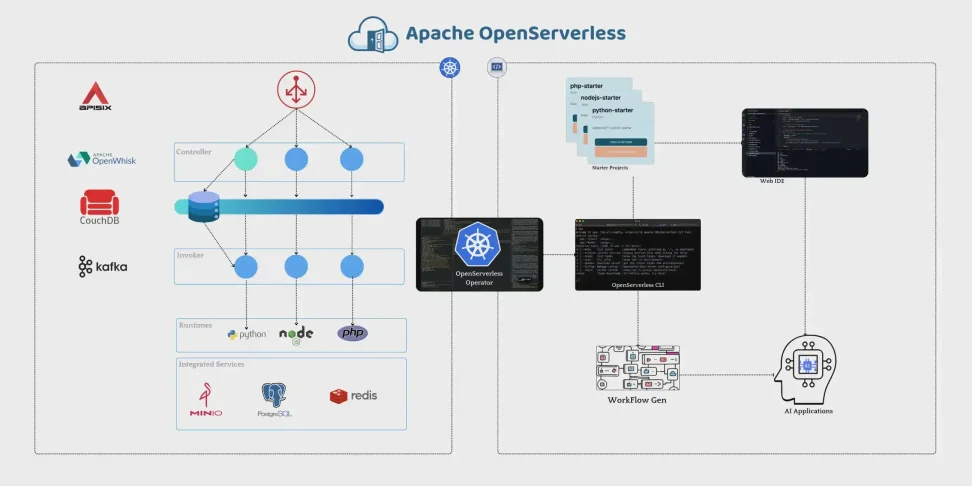
The move to serverless computing, or Function as a Service (FaaS), has revolutionized how developers build and deploy applications. By abstracting away the underlying infrastructure, it allows you to focus purely on code that runs in response to events. While cloud providers offer excellent FaaS platforms, a self-hosted solution like Apache OpenServerless gives you the same power on your own Kubernetes infrastructure, eliminating vendor lock-in and providing full control over your environment—a critical feature for modern AI workloads.
This guide will walk you through the core concepts, setup, and powerful capabilities of using an open serverless framework.
🧭 How to Understand the Serverless Model
At its heart, serverless means you no longer manage servers, virtual machines, or containers. You simply provide code (a “function”), and the platform handles everything required to run it whenever it’s triggered.
- Event-Driven: Functions lie dormant until an event occurs. This event-driven nature is the engine of a serverless application. Common event sources include:
- An HTTP request from a web or mobile app.
- A new file being uploaded to a storage bucket.
- A message arriving in a message queue (like Kafka or RabbitMQ).
- A change in a database record.
- A scheduled CRON trigger.
- Automatic Scaling & Cost Efficiency: The platform automatically scales the number of running functions to match the volume of incoming events, from zero to thousands and back down again. This means you only pay for the exact compute time your code uses, drastically reducing costs associated with idle servers.
| Aspect | Traditional Server Architecture | Serverless (FaaS) Architecture |
| Cost Model | Pay for idle time (24/7 server rental). | Pay only for execution time (per millisecond). |
| Scaling | Manual or complex auto-scaling groups. | Automatic, managed by the platform. |
| Maintenance | OS patching, security hardening, updates. | Managed by the platform. |
| Deployment Unit | Full application or microservice. | A single function or a small piece of code. |
⚙️ How to Install and Configure
Open serverless platforms are designed to run on top of Kubernetes, leveraging its power for orchestration and scaling.
Prerequisites
- A running Kubernetes cluster (minikube for local development, or a managed K8s service).
kubectlcommand-line tool configured to connect to your cluster.helmpackage manager for Kubernetes.
Installation and Configuration Steps
- Add Helm Repository: Add the official Helm chart repository for your chosen open serverless platform.
- Configure
values.yaml: Before installing, you can customize the deployment. This is where you connect it to your existing infrastructure, such as storage for function code, a Redis cluster for caching, or external databases. - Deploy with Helm: Use a single command to deploy all the necessary components (API gateway, controller, invokers) into your cluster.
Sample values.yaml Configuration |
| “`yaml |
| #– values.yaml: Customize the OpenServerless deployment | | # Enable persistence for function code and data | | persistence: | | enabled: true | | storageClass: “fast-ssd” # Your K8s StorageClass | | size: 20Gi | | | # Configure a connection to an external Redis for caching | | cache: | | enabled: true | | type: external | | redis: | | host: “my-redis-cluster.cache.svc.cluster.local” | | port: 6379 | | “` | |
📌 How to Explore AI Integration
One of the most powerful use cases for a self-hosted serverless platform is running AI and Machine Learning models. This approach gives you the scalability of serverless while ensuring your sensitive data never leaves your private infrastructure.
Why Self-Hosted Serverless AI?
- Data Privacy: Run inference on proprietary data using a private Large Language Model (LLM) without sending it to a third-party API.
- Cost Control: Avoid expensive per-token API charges for high-volume tasks. You control the hardware and scaling.
- Model Customization: Deploy fine-tuned or custom-built models that aren’t available on public platforms.
The architecture is simple: an event (like an API call) triggers a function that loads your AI model into a container, performs the inference, and returns the result. The platform handles warming up containers and scaling them based on real-time demand.
Writing and Deploying Your First Function
Once the platform is running, you can deploy code in minutes.
- Write Your Function: Create a simple Python function.
Code: hello.py |
| “`python |
| import json |
| def main(event, context): |
| “”” |
| A simple serverless function. |
| ‘event’ contains the trigger data. |
| “”” |
| name = event.get(‘name’, ‘World’) |
| greeting = f”Hello, {name}!” |
| return { |
| “statusCode”: 200, |
| “headers”: { ‘Content-Type’: ‘application/json’ }, |
| “body”: json.dumps({ ‘message’: greeting }) |
| } |
| “` |
- Deploy via CLI: Use the platform’s command-line tool to deploy the function.
| Command: Deploy Function |
| “`bash |
| # Deploy ‘hello.py’ as a function named ‘my-first-function’ |
| # The platform will create an HTTP endpoint to trigger it. |
| osls fn deploy my-first-function –runtime python:3.9 –file hello.py –trigger http |
| “` |
After deployment, the CLI will provide you with an HTTP endpoint. Accessing this endpoint in your browser or with curl will execute your function instantly, demonstrating the power and simplicity of the serverless model on your own terms.
More Topics
- How to Compare and Choose Modern Shells Beyond Bash
- How to Organize Large Photo Collections with KPhotoAlbum
- How to Build a Physical Computing Project with Raspberry Pi
- How to Safely Automate Sysadmin Tasks with Bash Scripts
- How to Install and Customize Deepin 25
- How to Create AI-Generated Images That Match Your Vision
- How to Design Logical Puzzles to Test AI Reasoning